What is the FEGLI for federal employees?
FEGLI stands for Federal Employees’ Group Life Insurance, which is a life insurance program for federal employees in the United States. It offers several types of life insurance coverage, including Basic, Option A (Standard Optional), Option B (Additional Optional), and Option C (Family Optional) coverage. Federal employees can choose different combinations of these options based on their needs.
Here’s a brief overview of the different coverage options under FEGLI:
- Basic Insurance: This is automatic coverage that provides a death benefit equal to the employee’s annual basic pay (rounded up to the next $1,000) plus $2,000. The cost of this coverage is shared between the employee and the federal government.
- Optional Insurance:
- Option A (Standard Optional): Provides an additional flat amount of coverage, $10,000, on top of the Basic Insurance.
- Option B (Additional Optional): Allows employees to elect coverage equal to one, two, three, four, or five times their annual basic pay (after rounding up to the nearest $1,000).
- Option C (Family Optional): Provides coverage for the employee’s spouse and eligible dependent children. There are several multiples available for this coverage, allowing employees to choose the amount of coverage they need for their family members.
The premiums for Optional Insurance (Options A, B, and C) are paid entirely by the employee, and the cost varies based on the employee’s age and the amount of coverage selected.
FEGLI is administered by the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) for federal employees, and it is an important benefit that provides financial security to employees and their families in the event of death.
What is the tax benefit from a life policy
Life insurance policies can provide several tax benefits, both during the policyholder’s lifetime and after their death. Here are some key tax benefits associated with life insurance policies in general (please note, specifics can vary by jurisdiction and policy type):
- Tax-free Death Benefit: One of the primary tax benefits of life insurance is that the death benefit paid to beneficiaries upon the insured’s death is typically income tax-free. This means your beneficiaries generally won’t have to pay federal income tax on the proceeds they receive from the life insurance policy.
- Tax-deferred Growth: For certain types of permanent life insurance policies (such as whole life or universal life), the cash value within the policy grows tax-deferred. This means you don’t pay taxes on the growth of the cash value as long as it remains inside the policy. This can allow the cash value to accumulate more quickly over time.
- Tax-free Loans: Policyholders may be able to take loans against the cash value of their permanent life insurance policy without triggering income tax, as long as the policy remains in force. These loans are not considered taxable income because they are technically loans against the policy’s value rather than income.
- Tax-free Partial Withdrawals: Similar to loans, policyholders may be able to withdraw a portion of the cash value of their permanent life insurance policy up to their basis (the total premiums paid into the policy) without paying income tax. This allows for access to funds without incurring immediate tax consequences.
- Estate Tax Benefits: Life insurance can also be used as a tool to provide liquidity for paying estate taxes. Proceeds from life insurance policies are generally not included in the insured’s estate for federal estate tax purposes, provided the policy is owned properly.
It’s important to note that tax laws can change, and the tax treatment of life insurance policies can vary based on the specific circumstances and the type of policy. Consulting with a tax advisor or financial planner who understands your individual situation and local tax laws is recommended to fully understand the tax implications of life insurance and how it fits into your overall financial plan.
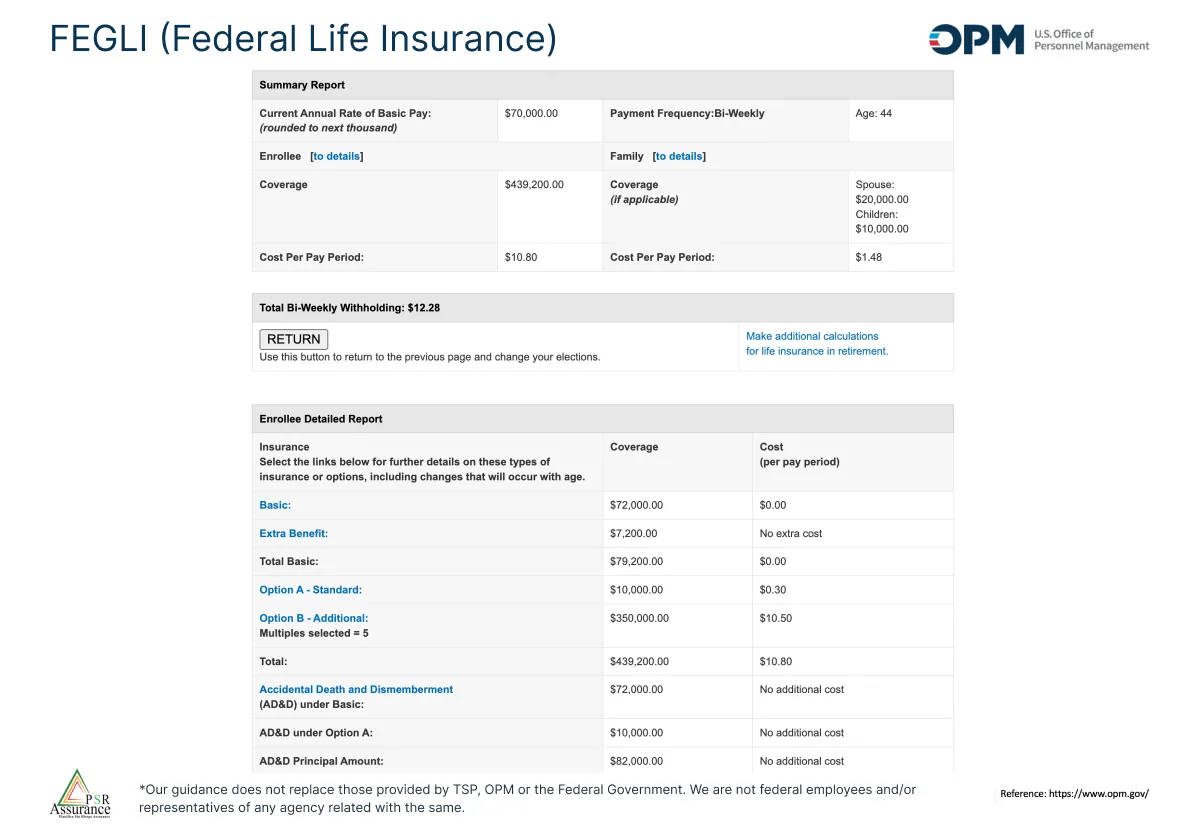
This part is the quote for a person with 45 years. A year salary $70,000. This employee has option A and B with 5 times his salary. His aportation by paid period is $10.80.
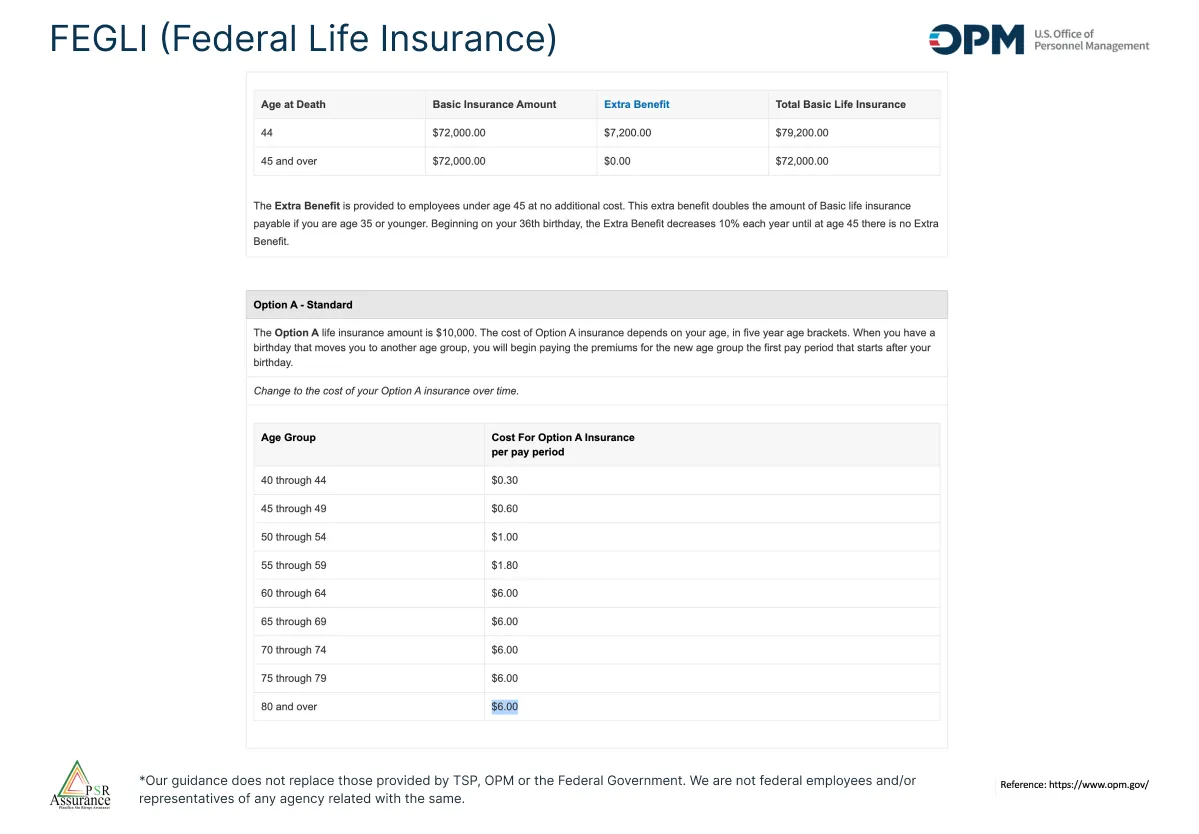
This image makes reference to the option A. This option is an extra Insurance benefit. This benefit has a yearly reduction until the 45 years when the benefit is over. But the cost of this benefit increases every 5 years until the 60 year when it reaches $6.00 monthly.
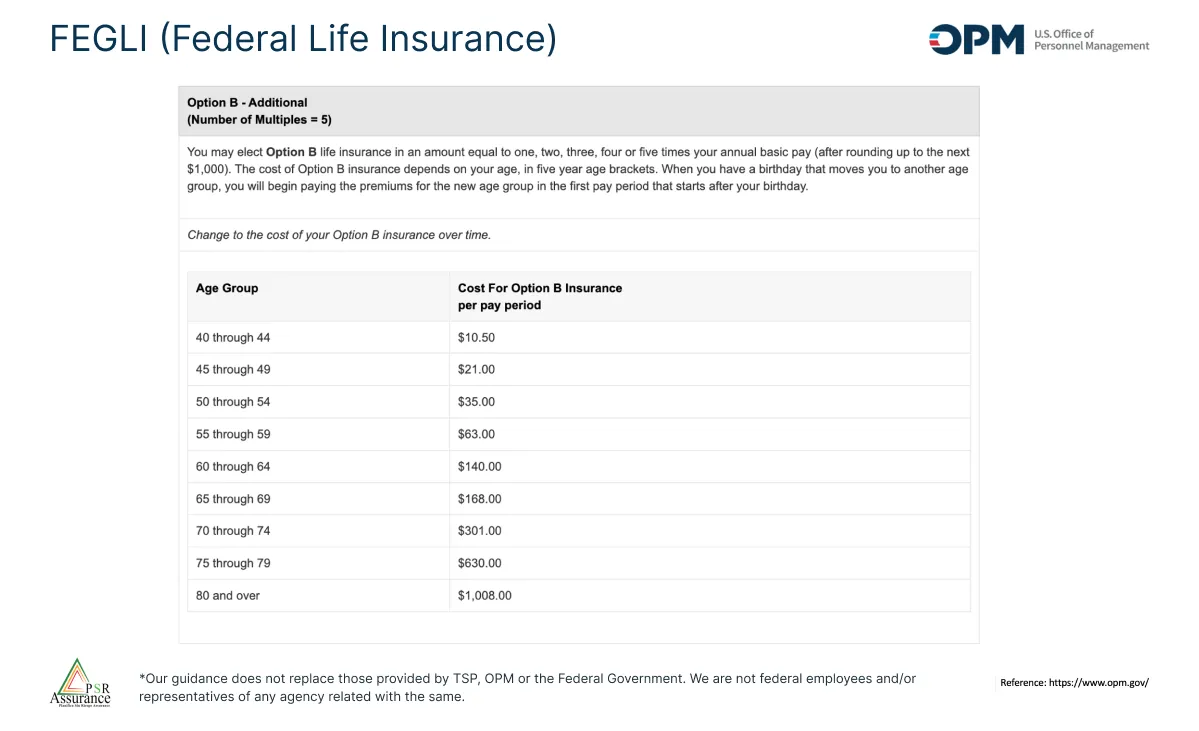
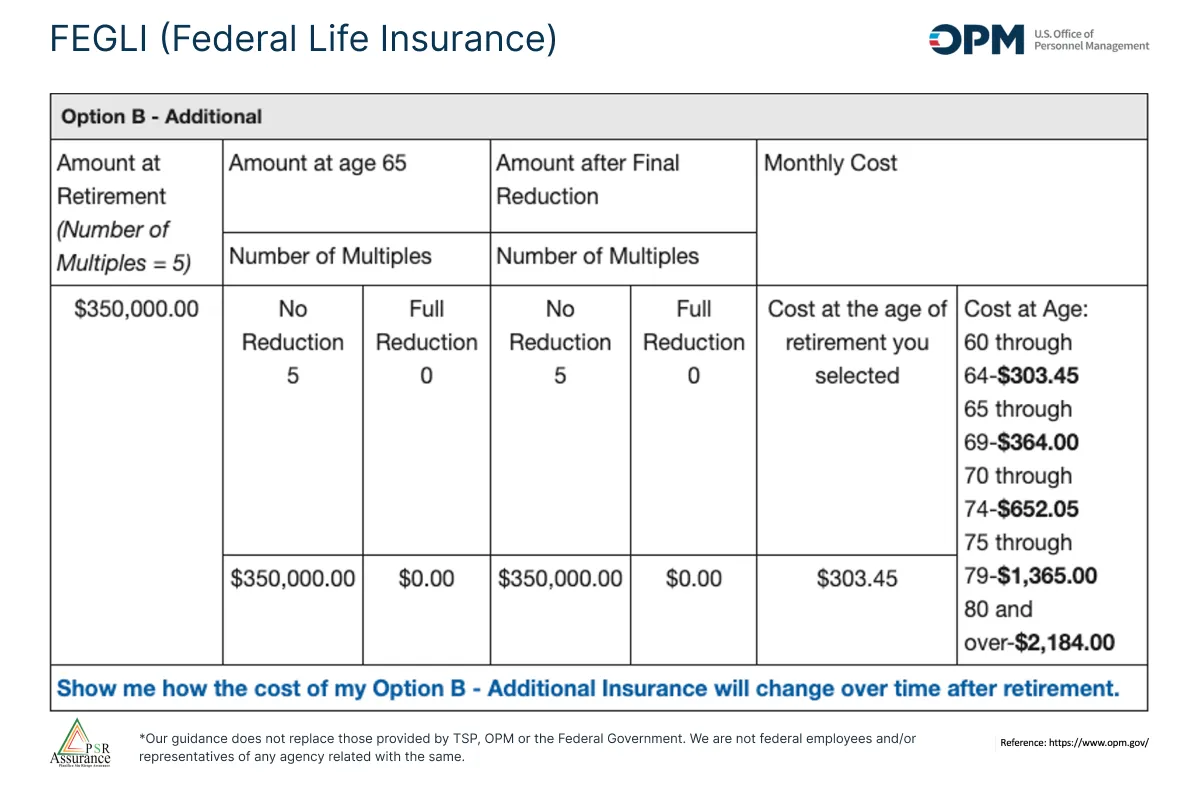
This image makes reference to option B. This option multiplied the salary of the client for the maximum of 5 times. This benefits the employee who has 100% of the aportation. This option increases the employee aportation every 5 years from the 45.
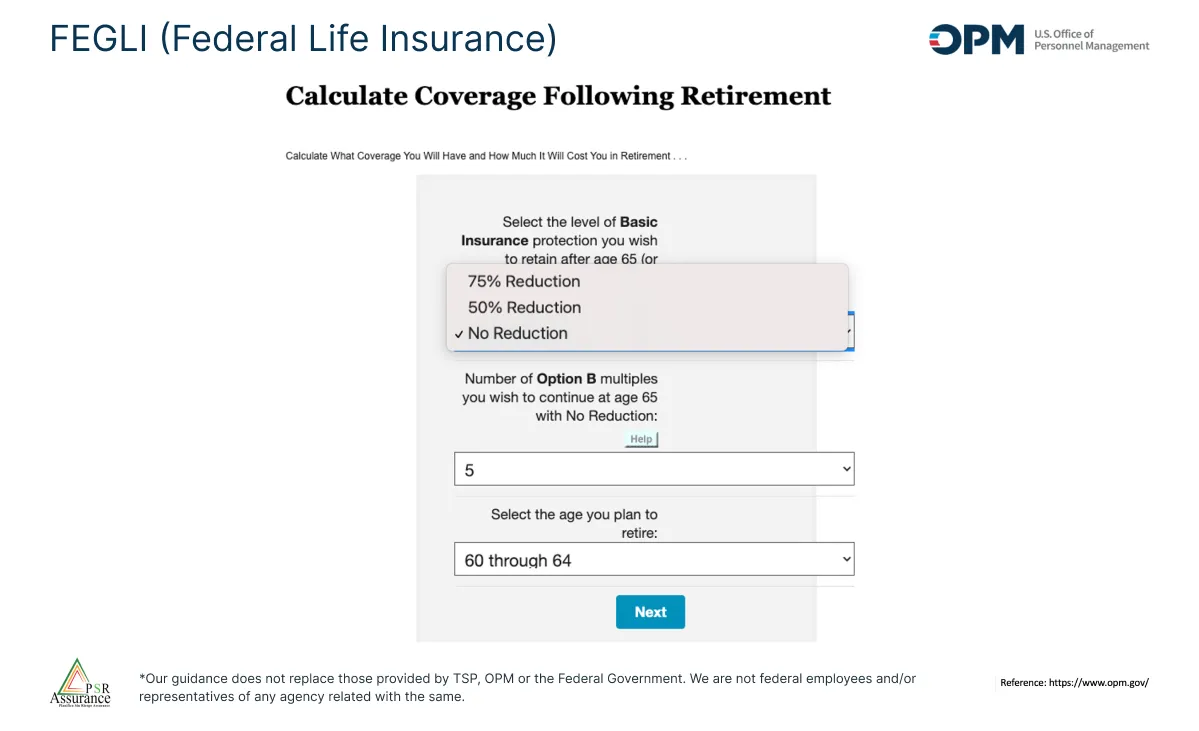
This image makes reference to retirement options. The employee has the opportunity to decide if to keep the life insurance or reduce it by 50% or 75% and leave option B or eliminate it.
This graphic shows what happens when the client retires with his life insurance if the client selects only the basic coverage with no reduction. The basic coverage is his annual salary. The total is the monthly employee contribution.

This graphic shows what happens if the employee keeps option B in his retirement. The cost at 60 age is going to be 303.45 plus $186.86 from the basic coverage. The option B increases every 4 like the graphic shows.
What option does the Federal Employees have?
Term life insurance. What is?
Term life insurance is a type of life insurance that provides coverage for a specific period, or term, of time. It is designed to provide financial protection for your beneficiaries (usually family members) in the event of your death during the term of the policy. Here are some key features of term life insurance:
- Coverage Period: Term life insurance policies are purchased for a specific period of time, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. The coverage ends when the term expires, unless it is renewed or converted to a permanent life insurance policy (if allowed by the terms of the policy).
- Death Benefit: If the insured person dies during the term of the policy, the insurance company pays a death benefit to the designated beneficiaries. This death benefit is typically a lump sum payment and is generally income tax-free for the beneficiaries.
- Affordability: Term life insurance is often more affordable than permanent life insurance (such as whole life or universal life) because it does not include a cash value component or investment features. Premiums are typically lower, especially for younger individuals in good health.
- Renewability and Convertibility: Many term life insurance policies offer the option to renew the policy at the end of the term, often at a higher premium rate. Some policies also include a convertibility feature, allowing the policyholder to convert the term policy into a permanent life insurance policy without undergoing a medical exam.
- No Cash Value: Unlike permanent life insurance policies, term life insurance policies do not accumulate cash value over time. This means that if the insured person outlives the policy term, no benefits are paid out (unless the policy is renewed or converted, if applicable).
- Purpose: Term life insurance is often chosen to provide financial protection during specific periods of financial responsibility, such as raising children, paying off a mortgage, or ensuring income replacement for a spouse. It can also be used to cover short-term debts or business obligations.
Term life insurance is straightforward and serves the primary purpose of providing financial security for loved ones in case of the insured’s death during a specified period. It’s important to carefully consider the length of coverage needed, the amount of coverage, and any optional features or riders that may be beneficial based on your individual circumstances and financial goals.
Whole Life insurance. How does it work?
Whole life insurance is a type of life insurance policy that provides coverage for the entire lifetime of the insured, as long as premiums are paid according to the terms of the policy. Here are the key features of whole life insurance:
- Lifetime Coverage: Whole life insurance is permanent insurance, meaning it covers the insured person for their entire life, from the date the policy is issued until the insured’s death, as long as premiums are paid. There is no specific term limit like there is with term life insurance.
- Fixed Premiums: The premiums for whole life insurance are typically fixed and do not change over the life of the policy. Premiums are determined based on the insured’s age, health status, and the amount of coverage chosen at the time of purchase. This provides predictability in budgeting for the insured and their beneficiaries.
- Cash Value Accumulation: A portion of each premium payment goes into a cash value account within the policy. This cash value grows on a tax-deferred basis over time. The growth rate is typically guaranteed and specified in the policy contract, ensuring that the cash value accumulates steadily.
- Guaranteed Death Benefit: Whole life insurance guarantees a death benefit that is paid to the beneficiaries upon the death of the insured. This death benefit is typically a lump sum payment and is generally income tax-free for the beneficiaries.
- Access to Cash Value: Policyholders can access the cash value of the policy through policy loans or withdrawals. Policy loans allow the policyholder to borrow against the cash value at a low interest rate, and withdrawals can be made up to the amount of premiums paid into the policy without triggering income taxes (although withdrawals in excess of premiums paid may be subject to taxes).
- Non-forfeiture Options: Whole life insurance policies often include non-forfeiture options, which provide alternatives if the policyholder stops paying premiums. These options may include using the cash value to purchase paid-up insurance, continue coverage for a reduced death benefit, or receive the cash surrender value of the policy.
- Dividends (for Participating Whole Life): Some whole life insurance policies are participating policies, meaning they may pay dividends to policyholders. Dividends are not guaranteed and depend on the insurer’s financial performance. Policyholders can choose how dividends are used, such as cash payments, reducing premiums, purchasing additional coverage, or increasing the cash value.
- Estate Planning and Wealth Transfer: Whole life insurance is often used as part of estate planning strategies to provide liquidity for estate taxes or to transfer wealth to heirs in a tax-efficient manner.
Whole life insurance is considered a conservative financial product that offers both a death benefit and a cash value accumulation component. It provides long-term financial protection and can serve as a tool for building savings and leaving a legacy for loved ones. However, it’s important to carefully evaluate the costs, benefits, and suitability based on individual financial goals and circumstances before purchasing a whole life insurance policy.
Index Universal Life Benefit
Index Universal Life (IUL) insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that combines the features of traditional universal life insurance with the opportunity to earn interest linked to the performance of a stock market index, such as the S&P 500. Here are the key benefits and features of Index Universal Life insurance:
- Permanent Life Insurance Coverage: Like other types of permanent life insurance, Index Universal Life provides coverage for the entire lifetime of the insured, as long as premiums are paid.
- Flexibility in Premium Payments: Policyholders can typically adjust their premium payments within certain limits, which provides flexibility to accommodate changes in financial circumstances.
- Cash Value Accumulation: A portion of the premium payments goes into a cash value account, which earns interest based on the performance of a selected stock market index (such as the S&P 500). The interest credited to the cash value account is linked to the index’s performance, subject to caps, floors, and participation rates set by the insurance company.
- Downside Protection: Unlike direct investments in the stock market, where losses can occur, IUL policies often provide downside protection. This means the cash value doesn’t decrease when the index performs poorly; it simply may not earn interest for that period.
- Potential for Higher Returns: If the selected index performs well, the cash value accumulation within the IUL policy can grow faster compared to traditional universal life insurance policies, which typically earn fixed or lower interest rates.
- Income Tax Benefits: Similar to other life insurance policies, the cash value growth in an IUL policy grows tax-deferred. This means you don’t pay taxes on the cash value growth until you withdraw it from the policy. Additionally, the death benefit paid to beneficiaries is generally income tax-free.
- Policy Loans and Withdrawals: Policyholders can access the cash value through policy loans or withdrawals, although loans may accrue interest and reduce the death benefit if not repaid. Withdrawals are typically tax-free up to the amount of premiums paid into the policy.
- Flexible Death Benefit Options: IUL policies often offer flexibility in death benefit options, allowing policyholders to adjust the death benefit amount over time to meet changing needs or estate planning goals.
- Riders and Additional Benefits: Depending on the insurance company and policy, IUL policies may offer optional riders or benefits for additional coverage, long-term care needs, or disability income.
It’s important to note that Index Universal Life insurance policies can be complex financial products, and the performance of the cash value is tied to the performance of the selected index, which may vary over time. Policyholders should carefully review the policy terms, including caps, floors, participation rates, and other features, to understand how the policy works and its potential benefits and risks. Consulting with a financial advisor or insurance professional can help determine if an Index Universal Life policy is suitable based on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and overall financial plant.
Guarantee Universal Life with cash out
Guaranteed Universal Life (GUL) with cash out option is a type of permanent life insurance policy that combines the affordability of universal life insurance with guaranteed death benefit protection and the flexibility to access a portion of the policy’s cash value under certain conditions. Here are the key features and benefits of Guaranteed Universal Life insurance with a cash out option:
- Guaranteed Death Benefit: GUL policies provide a guaranteed death benefit that is payable to the beneficiaries upon the death of the insured, as long as premiums are paid according to the policy terms. This death benefit is typically fixed and does not vary based on market performance or other factors.
- Fixed Premiums: Premiums for GUL policies are usually fixed for the life of the policy, providing predictability in premium payments. Premiums are set based on factors such as the insured’s age, health status, and the desired death benefit amount at the time of policy issuance.
- Cash Value Accumulation: While GUL policies are primarily focused on providing a death benefit, some policies may accumulate cash value over time. The cash value growth is typically guaranteed and may accrue interest at a fixed rate set by the insurance company.
- Cash Out Option: Some GUL policies offer a cash out option, which allows the policyholder to access a portion of the policy’s cash value while the insured is alive. The cash out option may be available after a certain number of years of policy ownership or when specific conditions are met, such as reaching a certain age or after a waiting period.
- Tax-Advantaged Growth: Similar to other permanent life insurance policies, the cash value accumulation in a GUL policy grows on a tax-deferred basis. This means that policyholders do not pay taxes on the cash value growth as long as it remains inside the policy.
- Policy Loans and Withdrawals: Depending on the policy’s terms, policyholders may have the ability to take out policy loans against the cash value or make withdrawals. Policy loans typically accrue interest and may reduce the death benefit if not repaid, whereas withdrawals are generally tax-free up to the amount of premiums paid into the policy.
- No Lapse Guarantee Option: Some GUL policies may offer a “no lapse guarantee” rider, which ensures that the policy remains in force as long as the required premiums are paid. This guarantee can provide additional peace of mind by protecting against policy lapses due to insufficient cash value or missed premium payments.
- Flexibility in Coverage: GUL policies often offer flexibility in adjusting the death benefit amount or changing premium payment schedules, subject to certain limitations and conditions outlined in the policy contract.
Guaranteed Universal Life insurance with a cash out option is designed to provide a combination of permanent life insurance protection and the potential for accessing cash value for financial needs during the insured’s lifetime. As with any insurance product, it’s essential to review the specific features, costs, and benefits of the policy with a licensed insurance professional to determine if it aligns with your financial goals and needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Managing your Thrift Savings Plan (TSP) can be complex, but numerous resources and support options are available to help you navigate your retirement savings plan. Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) and answers to guide you:


